What Do Therapists Mean When They Say That They Apply A Deep Tissue Massage?
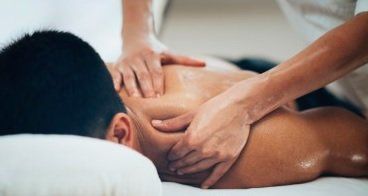
How Does Deep Tissue Massage Differ to A Relaxing Massage?
Deep tissue massage is a form of therapeutic bodywork that focuses on realigning deeper layers of muscles and connective tissue. The Leagrave Therapy Clinic provides clients with a deep tissue massage which involves the use of slow, firm pressure that is often applied with the therapist's hands, forearms, knuckles or elbows to target areas of chronic tension, muscle knots and adhesions. This is unlike a relaxation massage, which uses light to moderate pressure and a soothing rhythm,
The term “deep tissue” refers not only to the depth of pressure applied, but also to the depth of the layers affected, namely the deep fascia and muscle layers that lie beneath superficial muscles. When we say “deep tissue massage,” we typically mean a manual therapy technique that incorporates sustained pressure, often applied with the therapist’s fingers, knuckles, forearms, or elbows. This pressure is deliberately deeper than what one experiences in a Swedish massage but is always adapted to remain within the client’s pain tolerance. Communication between the therapist and the client is essential throughout the session to ensure that the pressure remains therapeutic and not painful. The use of elbows and reinforced hands allows for the delivery of controlled pressure to small, tight areas without causing strain to the therapist or discomfort to the client.
When To Attend For a Deep Tissue Sports Massage?
Deep tissue massage is commonly used to treat musculoskeletal issues such as chronic tension, sports injuries, postural problems and repetitive strain. It is especially beneficial for managing muscular trigger points (or knots) which are muscular bands of painful, rigid tissue that can disrupt circulation and limit movement. By physically manipulating these tissues, massage can help restore mobility and reduce pain. The therapy is often recommended for people suffering from conditions like sciatica, fibromyalgia or tension headaches that stem from muscular imbalances.
Safety
Safety is a major concern in any form of manual therapy, and deep tissue massage is generally considered safe when performed by a trained, licensed practitioner. It should not be overly painful, though some post-session soreness is common and typically subsides within a day or two. People with certain medical conditions such as blood clotting disorders, open wounds, or recent surgery should consult a healthcare provider before undergoing deep tissue work.
Research
Research into the effectiveness of deep tissue massage has grown in recent years. Multiple studies have found that deep tissue massage can significantly reduce pain and improve function in patients with chronic musculoskeletal disorders.
A study published in the Scientific World Journal by Majchrzychki et al., (2014) found that deep tissue massage (DTM) was effective in reducing lower back pain and that DTM was comparable to non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), but without the side effects.
Another study by Field et al., (2005) in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry suggested that deep tissue massage could also reduce stress hormone levels and increase serotonin and dopamine, which can enhance overall mood and well-being.
Additionally, clinical research has shown that deep tissue massage may improve joint mobility by reducing stiffness in surrounding soft tissues. A study by Srokowska et al., (2019) found that deep tissue massage is an effective method in the treatment of pain located in the thoracic spine as it the treatment can improve spinal joint mobility, help lengthen chest muscles including the pectoralis major, especially in people who perform long hours working in a sitting position.
Deep tissue massage can be particularly helpful for individuals with arthritis or limited joint range of motion due to past injuries. A small study by Zhang et al., (2024) found that massage therapy, as a stand-alone treatment, reduces pain, improves (joint) function and reduces medial muscle co-contraction in individuals with medial knee osteoarthritis (KOA).
Deep tissue sports massage can help by promoting better circulation, flushing out metabolic waste and stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system which can promote relaxation and healing. Weerapong et al., (2012) concluded that massage can help change parasympathetic activity (measured by heart rate, blood pressure and heart rate variability) and hormonal levels (measured by cortisol levels). They found that the treatment can promote a 'relaxation response' by reducing anxiety and improve mood post massage.
Summary
Deep tissue sports massage is a targeted, evidence-supported therapy designed to address chronic muscle tension, pain, and stiffness by applying deep but tolerable pressure to the body’s soft tissues. It is a safe and effective option for many people when performed properly and its benefits are supported by growing scientific research. As awareness of bodywork and integrative health practices continues to expand, deep tissue massage remains valuable for those seeking relief from muscular pain and improved physical function.
Massage Techniques:
References
Field, T., Hernandez-Reif
, M., Diego
, M., Schanberg
, S., Kuhn
, C. (2005) Cortisol decreases and serotonin and dopamine increase following massage therapy, International Journal of Neuroscience, 15; 10.
Majchrzycki, M., Kocur, P., Kotwicki, T. (2014) Deep Tissue Massage and Nonsteroidal Anti-InflammatoryDrugs for Low Back Pain: A Prospective Randomized Trial
, The Scientific World Journal; Hindawi Publishing Corporation: 1-7.
Srokowska, A., Bodek, M., Kurczewski, M., Srokowski, G., Siedlaczek, M., Lewandowski, A. (2019) Deep Tissue Massage and Mobility
and Pain in the Thoracic Spine
, 11 (2): 99-108.
Weerapong, P., Hume, P. A., Kolt, G. S. (2012) T he Mechanisms of Massage and Effects on Performance, Muscle Recovery and Injury Prevention, 35; 235-256.
Zhang, M., Liu, A., Pan, F., Lu, J., Zhan, H., Jones, R. K., The effectiveness of massage on pain, external knee adduction moment, and
muscle Co-contraction in individuals with medial compartment
knee osteoarthritis
, Journal of Bodywork & Movement Therapies; 40: 1672-1678.



